71 Exponential Parent Function YouTube
Graphing exponential functions (parent functions) - YouTube © 2023 Google LLC We'll build a simple table of values and then graph y = 2^x and then y = (1/2)^2, which are the basic exponential.

Big Blue Book of Parent Functions Exponential YouTube
Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more.
PPT PARENT FUNCTIONS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2019169
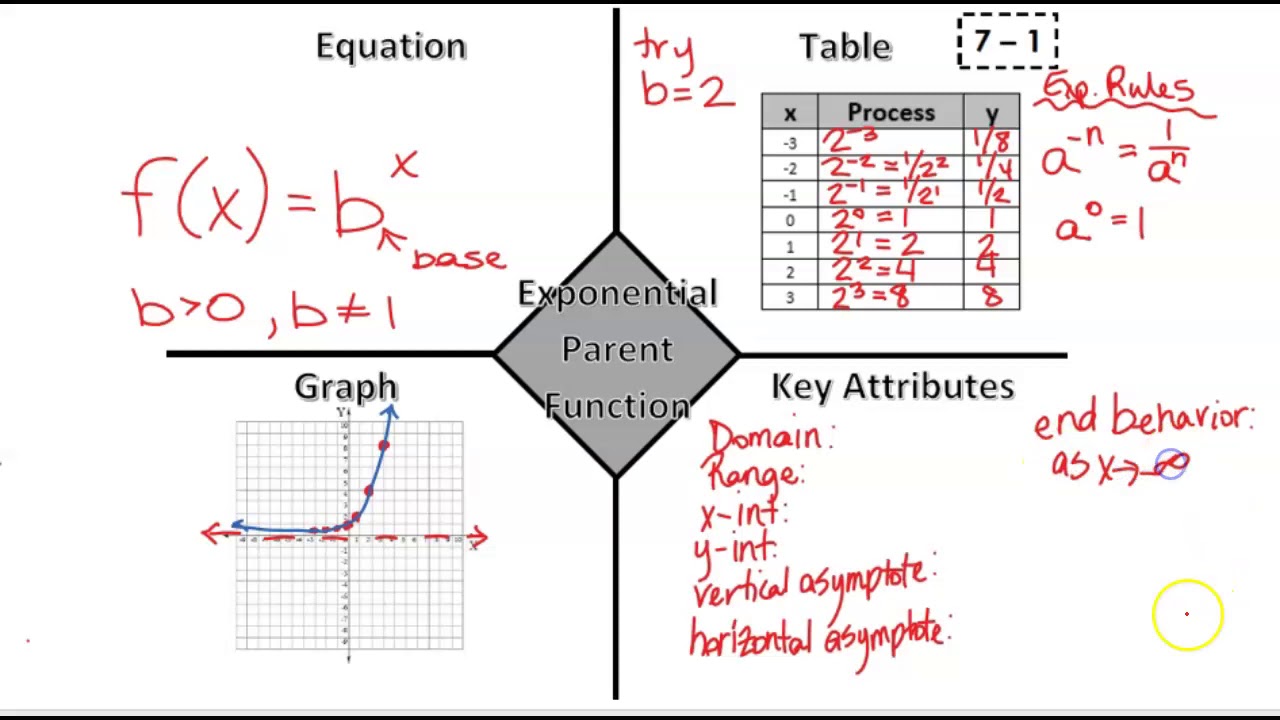
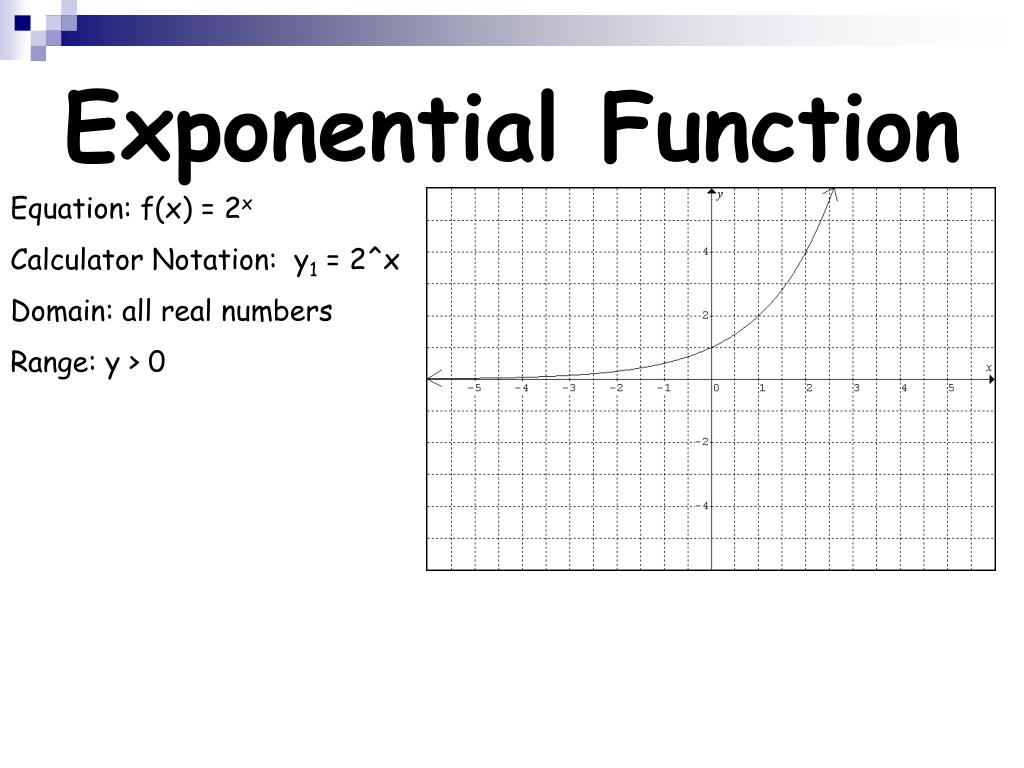
The domain of f(x) = 2x is all real numbers, the range is (0, ∞), and the horizontal asymptote is y = 0. To get a sense of the behavior of exponential decay, we can create a table of values for a function of the form f(x) = bx whose base is between zero and one. We'll use the function g(x) = (1 2)x.
PPT PARENT FUNCTIONS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2019169
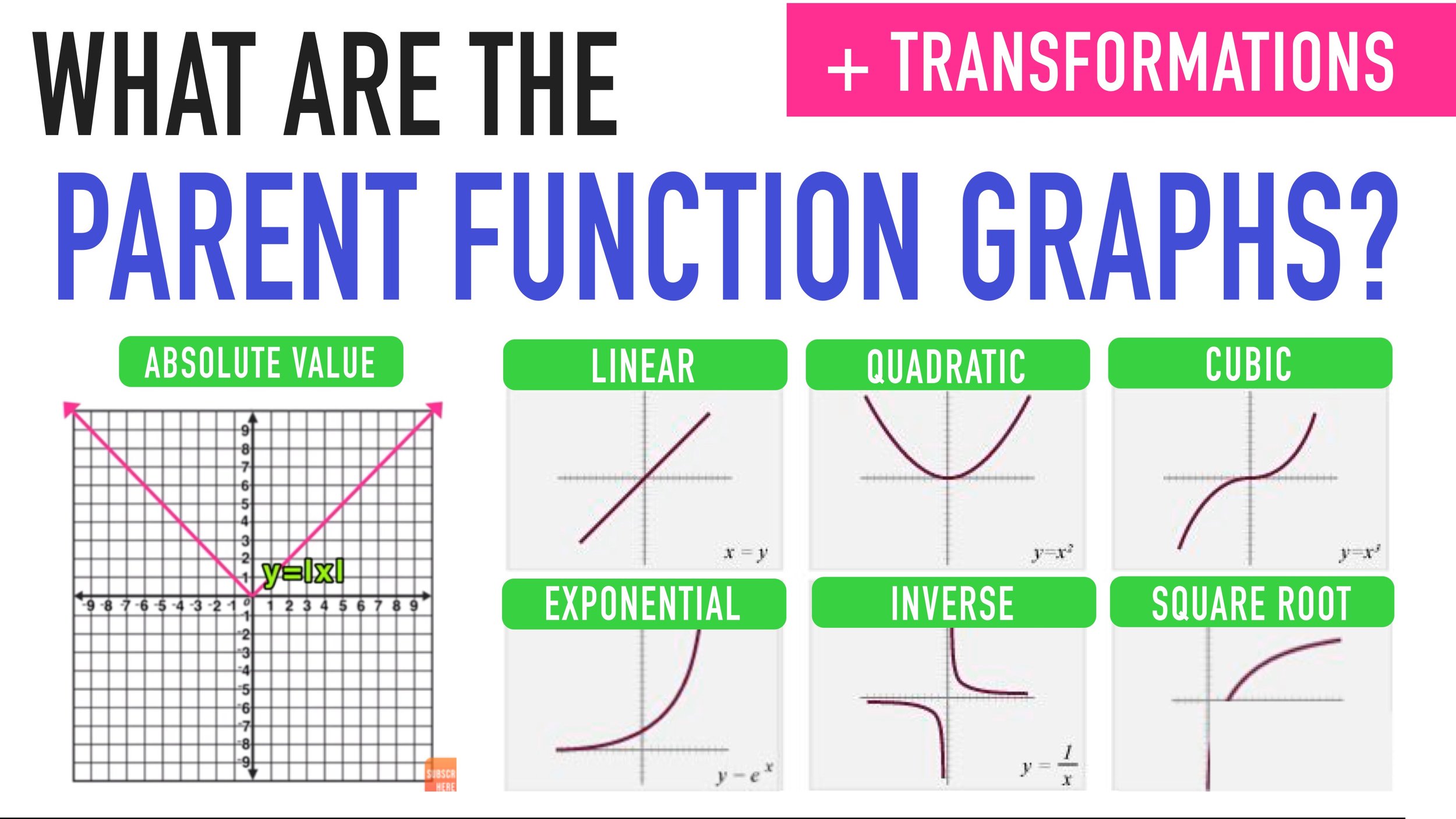
A parent function represents a family of functions' simplest form. This definition perfectly summarizes what parent functions are. We use parent functions to guide us in graphing functions that are found in the same family. In this article, we will: Review all the unique parent functions (you might have already encountered some before).
Exponential Functions. Transformations and Applications IntoMath
The "parent" function for this family is \(f(x) = x^2.\) Similar to the absolute value function, this function has a graph that appears to have two branches reaching upward, since anything squared is positive, but it takes on more of a "U" shape since it curves smoothly around the base. All quadratic functions have this same basic shape.
Graphing exponential functions (parent functions) YouTube
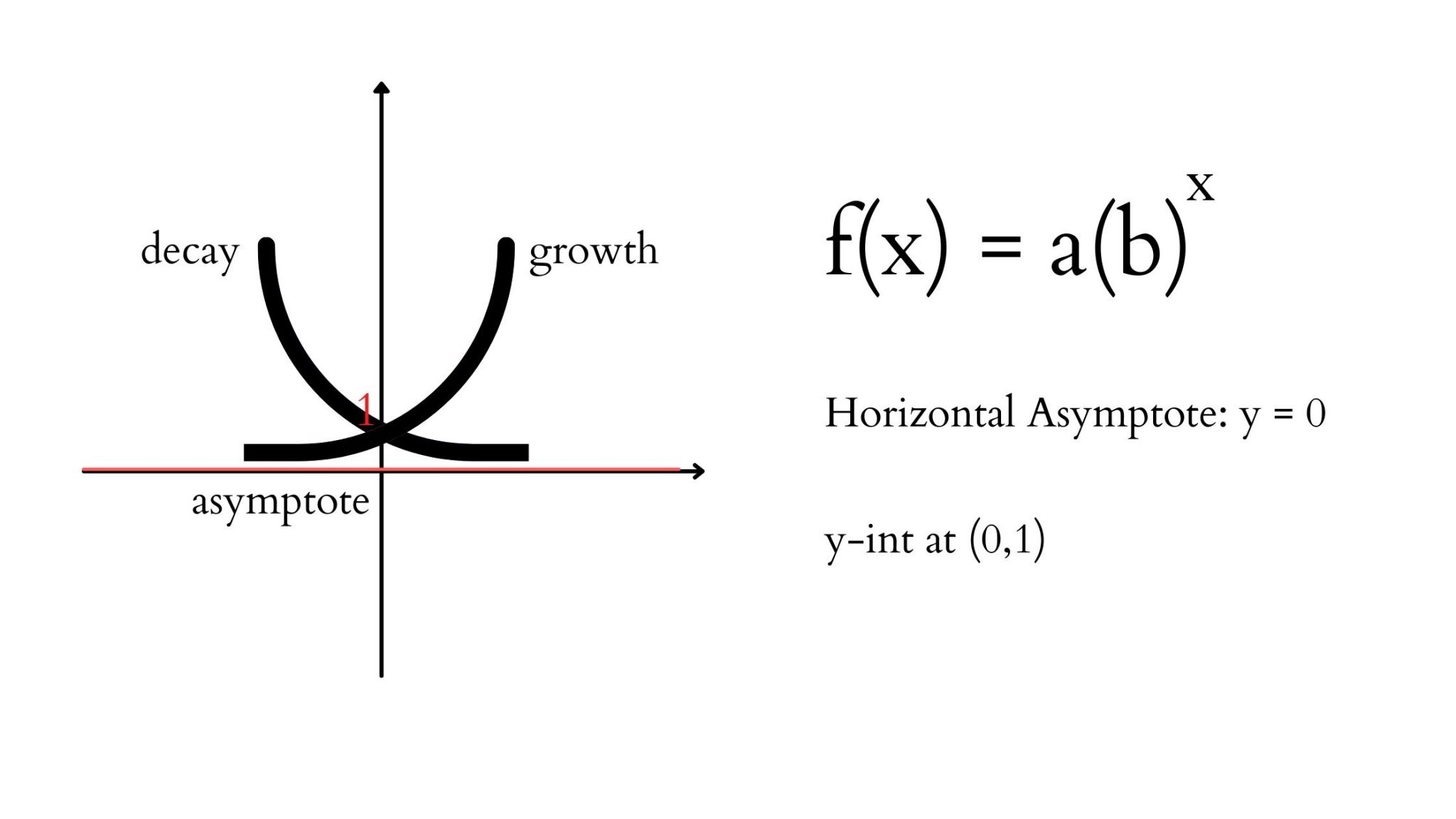
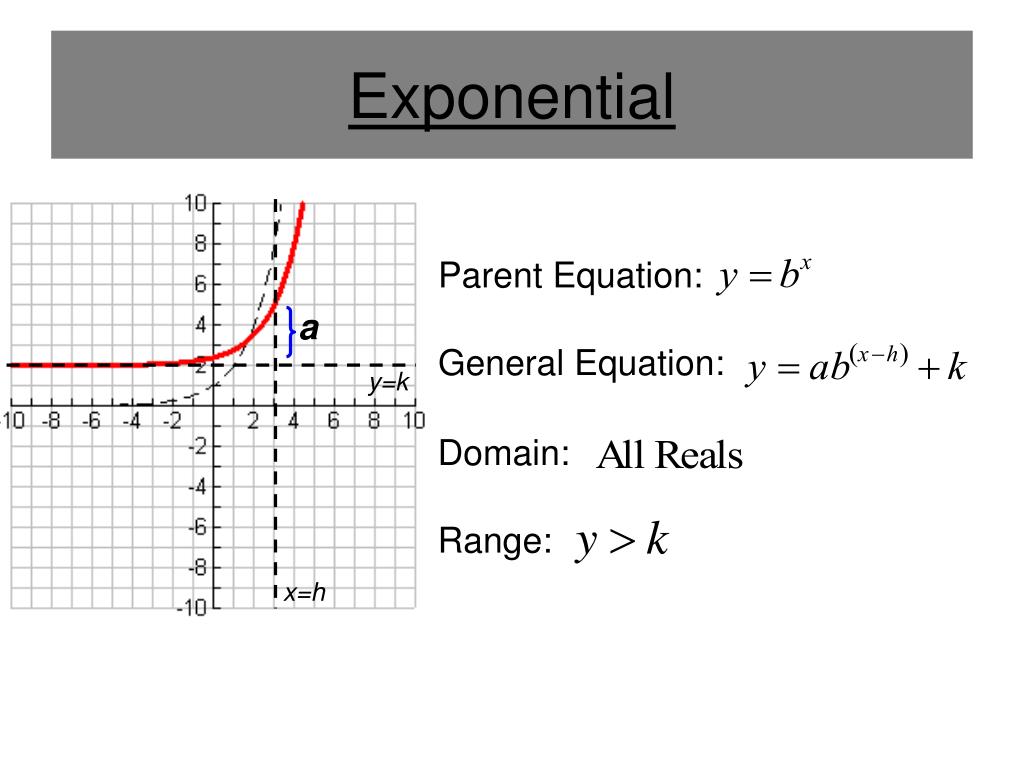
The range of an exponential function can be determined by the horizontal asymptote of the graph, say, y = d, and by seeing whether the graph is above y = d or below y = d. Thus, for an exponential function f (x) = ab x, Domain is the set of all real numbers (or) (-∞, ∞). Range is f (x) > d if a > 0 and f (x) < d if a < 0.

Parent Function Posters Lindsay Bowden
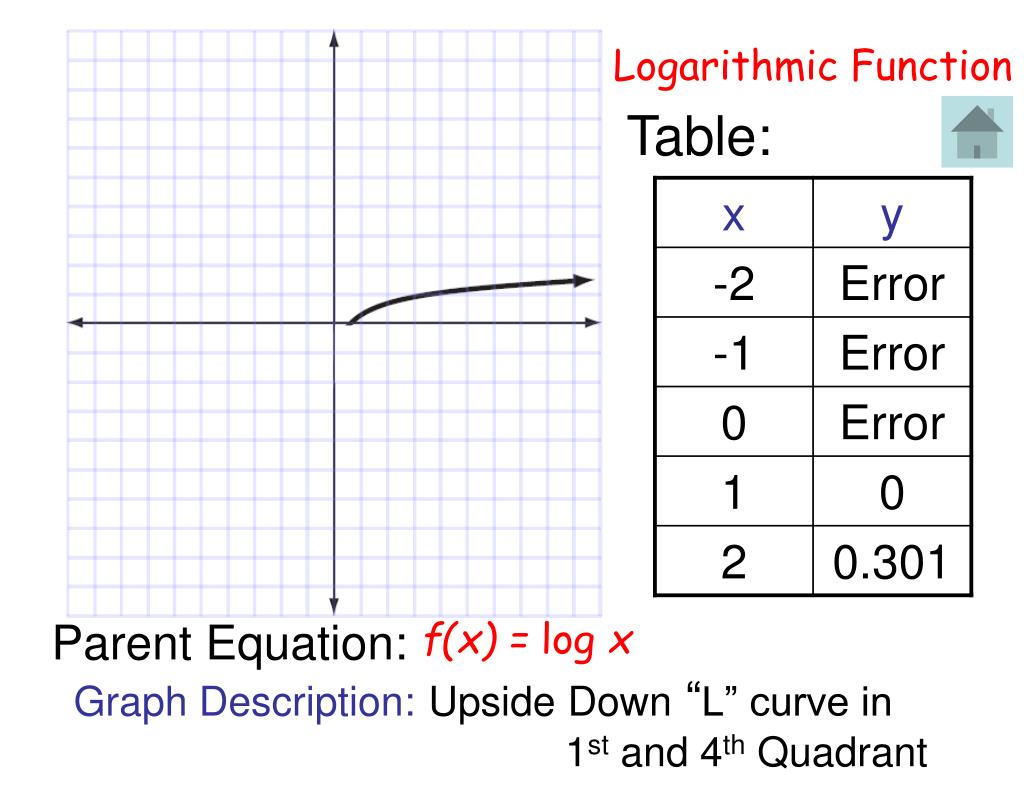
The asymptotes for exponential functions are always horizontal lines. Point 2: The y-intercepts are different for the curves. Finding the location of a y-intercept for an exponential function requires a little work (shown below). To determine the y-intercept of an exponential function, simply substitute zero for the x-value in the function.
PPT Parent Functions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2576658
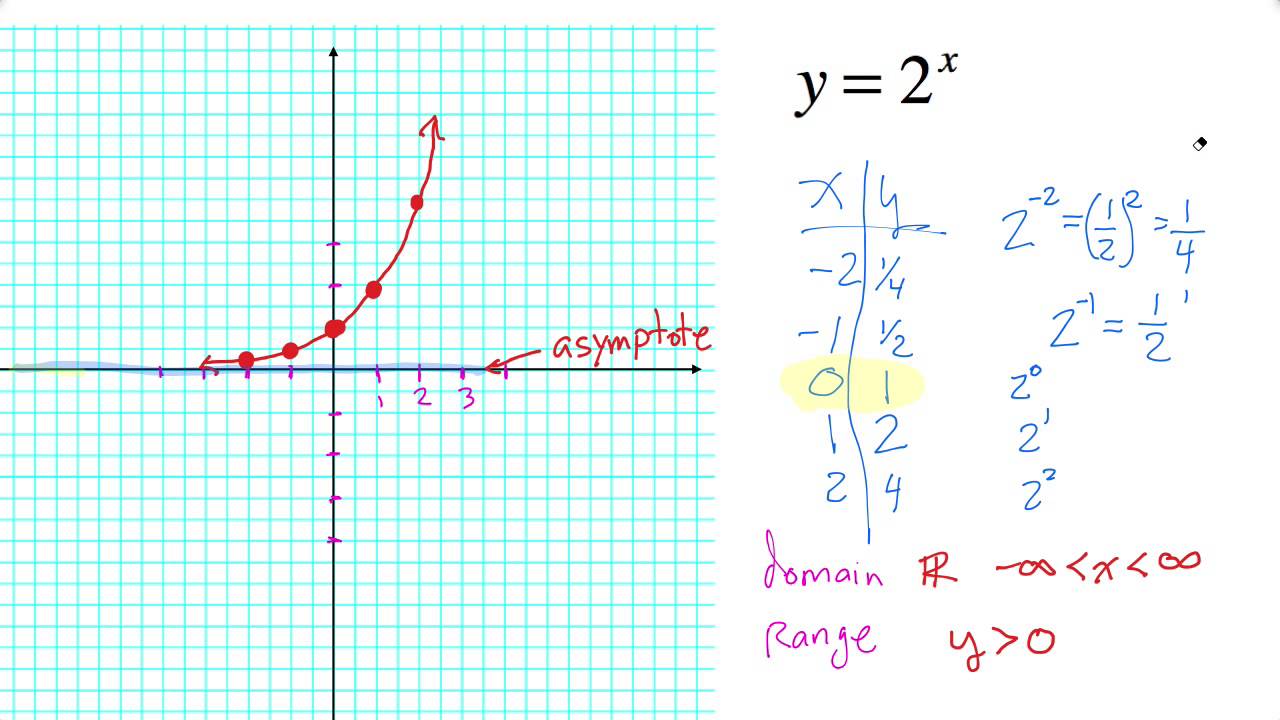
Graph Basic Exponential Functions. Exponential growth is modelled by functions of the form f(x) = bx where the base is greater than one. Exponential decay occurs when the base is between zero and one. We'll use the functions f(x) = 2x and g(x) = (1 2)x to get some insight into the behaviour of graphs that model exponential growth and decay.
Parent Functions and Parent Graphs Explained — Mashup Math
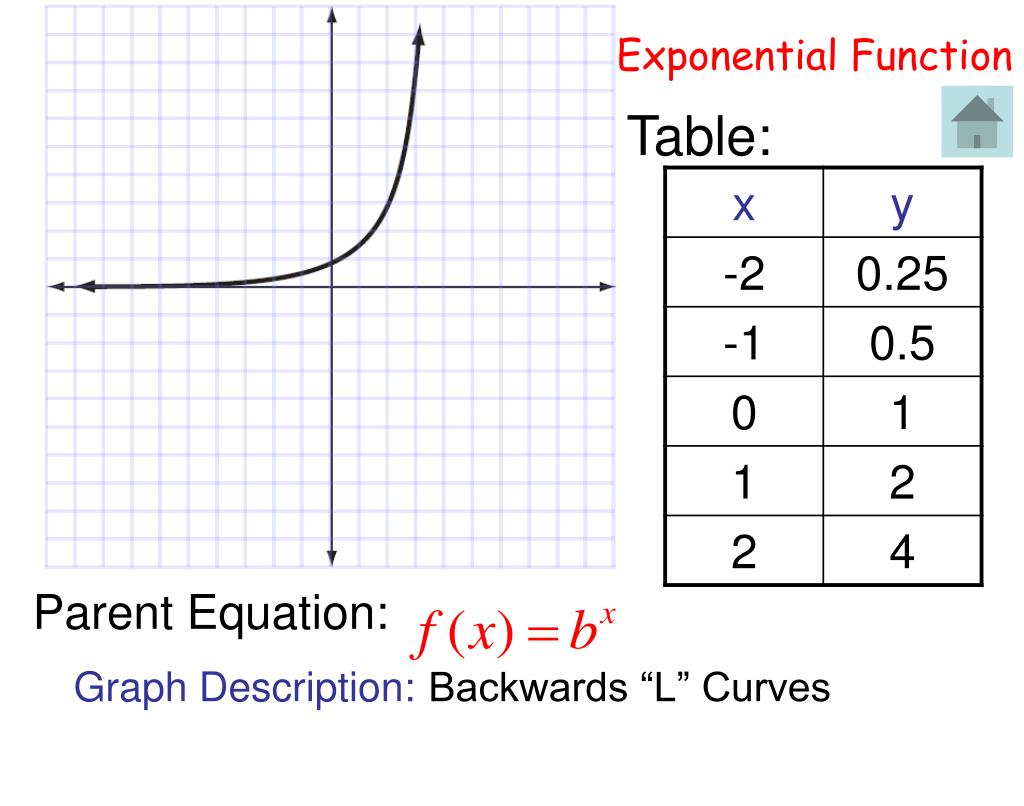
An exponential function represents the relationship between an input and output, where we use repeated multiplication on an initial value to get the output for any given input. Exponential functions can grow or decay very quickly.

PPT Objectives Be able to graph the exponential growth parent
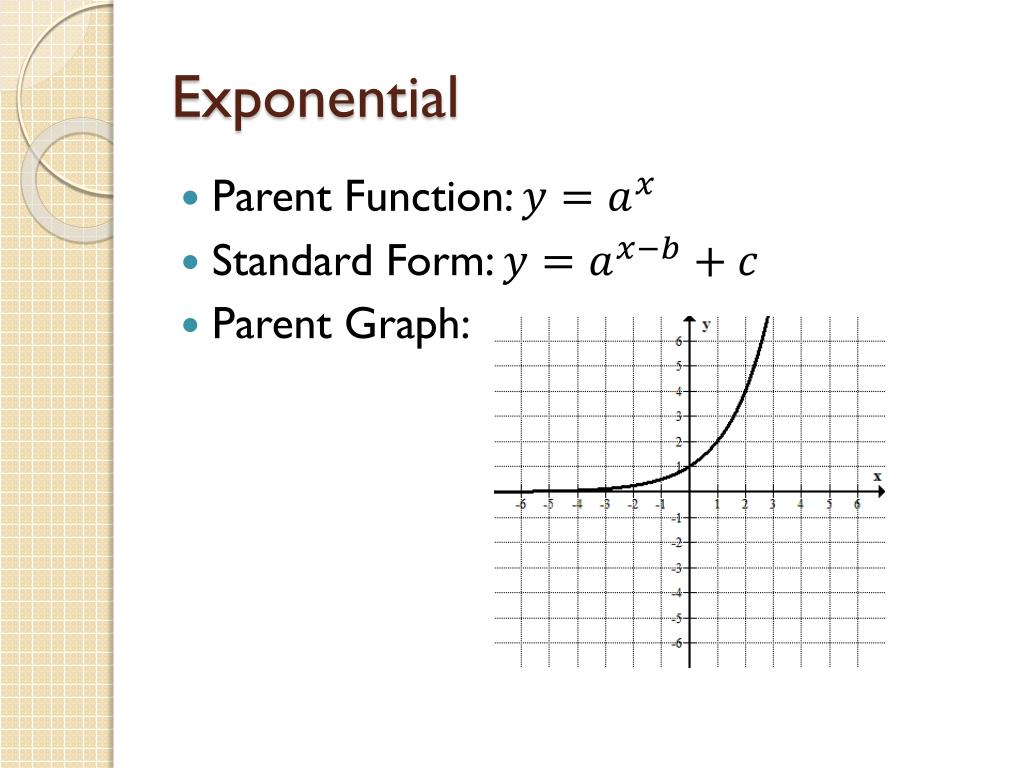
Definition: A parent function is the most basic function from which a family of similar functions is derived. By performing various operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc. on a parent function you obtain a function that belongs to the same family. Parent function graphs are the graphs of the respective parent function.
PPT Function Transformations PowerPoint Presentation, free download
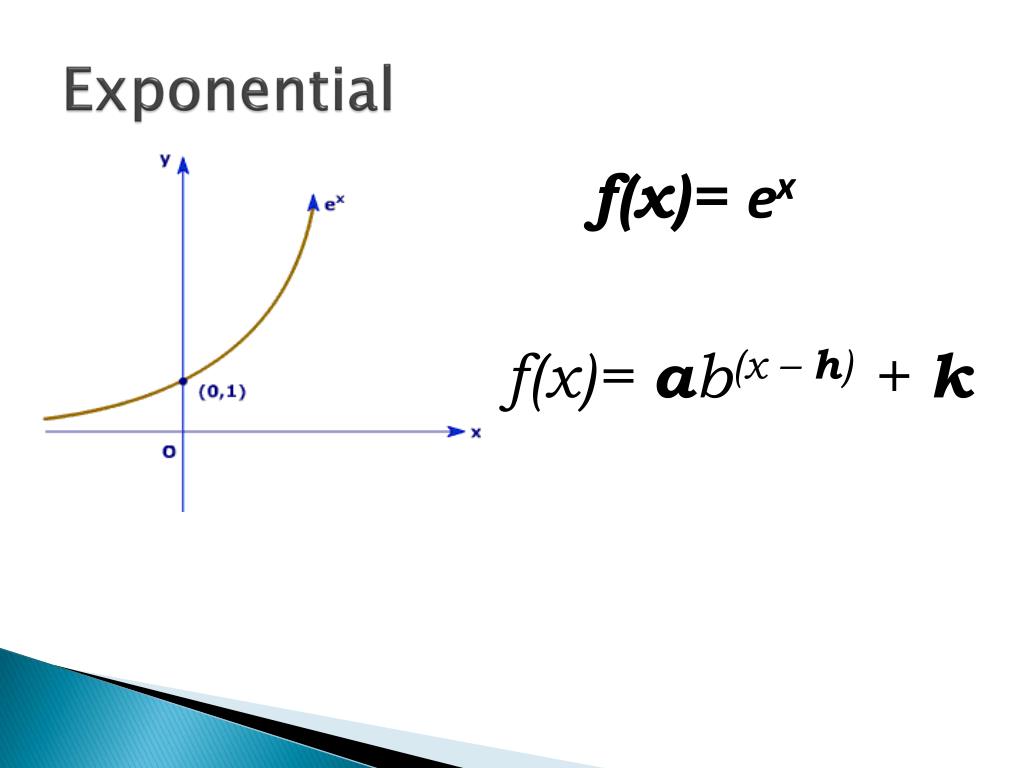
This is a parent function for the exponential function. The "2" is called the base; an exponential function can have any number as its base.. Exponential functions do not have vertices, but they do have a horizontal asymptote: a horizontal line which the graph will get very, very close to. 3. Pay close attention to the key points: x- and y.
PPT Parent Functions & Transformations PowerPoint Presentation ID
Unit 1 Polynomial arithmetic Unit 2 Complex numbers Unit 3 Polynomial factorization Unit 4 Polynomial division Unit 5 Polynomial graphs Unit 6 Rational exponents and radicals Unit 7 Exponential models Unit 8 Logarithms Unit 9 Transformations of functions Unit 10 Equations Unit 11 Trigonometry Unit 12 Modeling Course challenge

Exponential Parent Functions
For exponential functions, get the new asymptote by setting $ y=$ the vertical shift. The domain is always $ \left ( {-\infty ,\infty } \right)$, and the range changes with the vertical shift. Here are some examples, using t -charts, as we saw in the Parent Graphs and Transformations section: Transformation. T-chart.
PPT Parent Functions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3924112
8. Table 1. Each output value is the product of the previous output and the base, 2. We call the base 2 the constant ratio. In fact, for any exponential function with the form f (x) = ab is the constant ratio of the function. This means that as the input increases by 1, the output value will be the product of the base and the previous output.
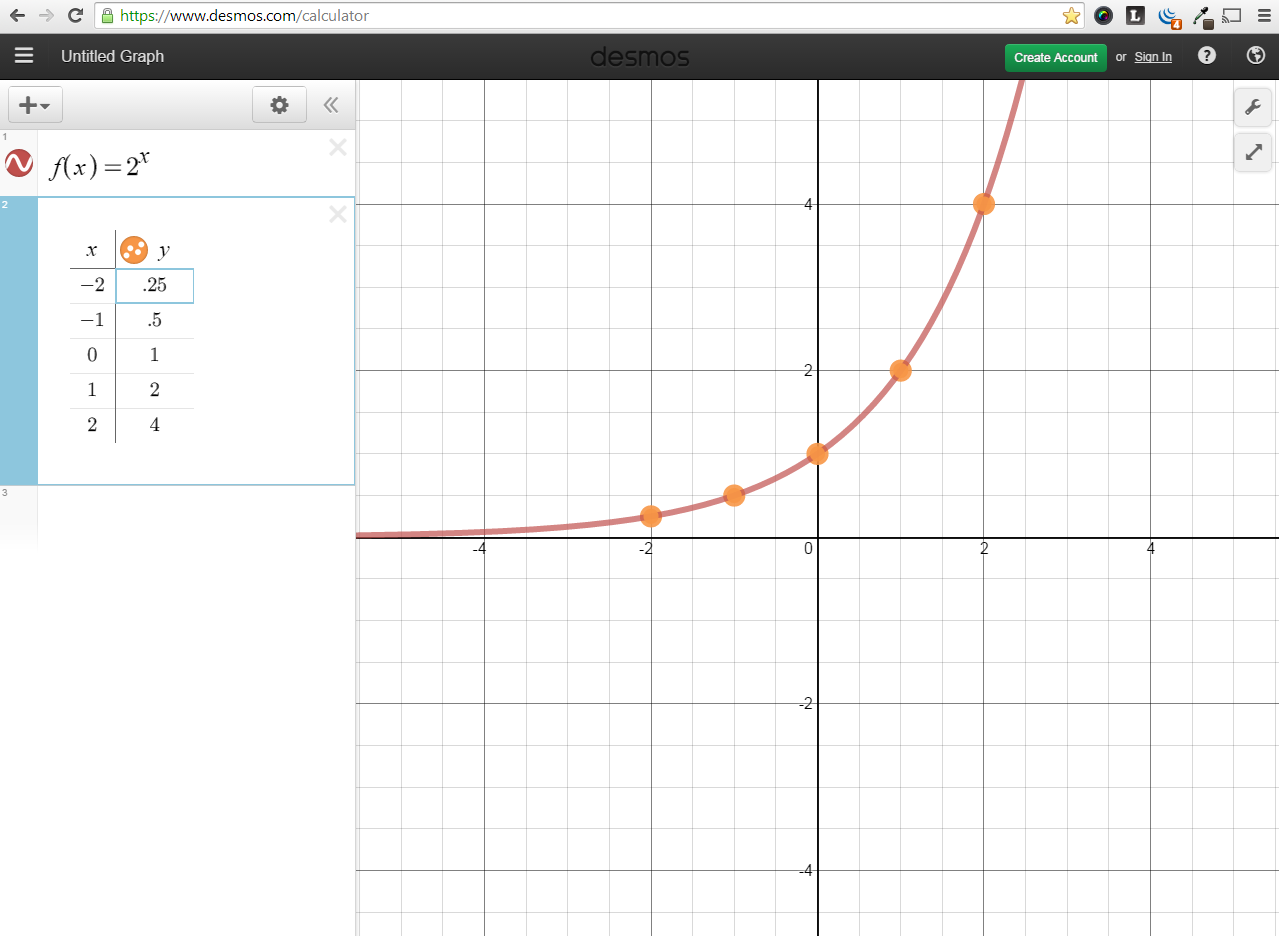
Exponential Functions Systry
Exponential functions are one-to-one functions. • graph crosses the y -axis at (0,1) • when b > 1, the graph increases • when 0 < b < 1, the graph decreases • the domain is all real numbers • the range is all positive real numbers (never zero) • graph passes the vertical line test for functions

Exponential Functions Cuemath
Custom Solutions Log In Exponential functions follow all the rules of functions. However, because they also make up their own unique family, they have their own subset of rules. The fo